Instructional design
Title: The Art and Science of Instructional Design
In the ever-evolving landscape of education and training, instructional design emerges as a crucial element bridging the gap between information delivery and effective learning. This multidisciplinary field combines psychology, education, and technology to create structured, engaging, and learner-centric experiences. In this article, we delve into the essence of instructional design, exploring its key components and its impact on the learning process.
Understanding Instructional Design:
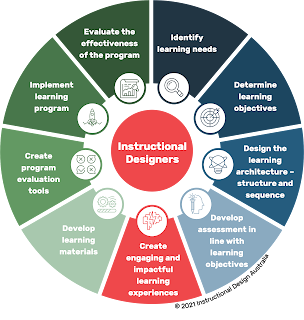
At its core, instructional design is the systematic process of developing instructional materials and activities that facilitate learning. It's more than just creating content; it's about understanding the learner's needs, crafting engaging experiences, and ensuring the transfer of knowledge. The process typically involves analysis, design, development, implementation, and evaluation—commonly known as the ADDIE model.
1. Analysis:
Before creating any learning material, instructional designers conduct a thorough analysis. This involves understanding the target audience, their prior knowledge, learning preferences, and the specific objectives of the instruction. This foundational step sets the stage for a tailored and effective learning experience.
2. Design:
The design phase focuses on structuring the content in a way that aligns with the identified objectives. This includes defining the scope, creating learning objectives, and deciding on the most appropriate instructional strategies. Designers also consider the overall aesthetics and user experience to enhance engagement.
3. Development:
With the blueprint in place, the development phase involves creating the actual learning materials. This could range from traditional textbooks to interactive e-learning modules, simulations, or multimedia presentations. The emphasis here is on aligning the content with the instructional design principles established earlier.
4. Implementation:
The implementation phase is the deployment of the instructional materials for the learners. This could happen in a physical classroom, through online platforms, or a blended approach. The key is to ensure that the delivery method aligns with the designed experience and reaches the intended audience effectively.
5. Evaluation:
Evaluation is an ongoing process throughout the instructional design cycle. It involves assessing the effectiveness of the instruction in meeting the learning objectives. Feedback from learners, performance metrics, and other assessment tools help refine and improve future iterations of the instructional design.
Key Principles of Instructional Design:
Several principles guide instructional designers in creating effective learning experiences:
1. Learner-Centered Approach:
Placing the learner at the center is fundamental. Understanding the learners' needs, motivations, and prior knowledge informs the design process, ensuring that the instruction is relevant and engaging.
2. Clear Learning Objectives:
Clearly defined learning objectives provide a roadmap for both the designer and the learner. Objectives guide content creation and help learners understand what is expected of them.
3. Multimodal Learning:
Recognizing that individuals have different learning preferences, instructional designers incorporate various modes of instruction—visual, auditory, kinesthetic—to cater to diverse learning styles.
4. Feedback Mechanisms:
Effective feedback is essential for learning. Whether through assessments, quizzes, or interactive activities, timely feedback helps learners understand their progress and areas for improvement.
5. Applicability and Real-world Context:
Relating learning to real-world scenarios enhances retention. Instructional designers strive to create content that learners can apply in practical situations, promoting a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
The Role of Technology in Instructional Design:
In the digital age, technology plays a pivotal role in instructional design. E-learning platforms, virtual reality, and interactive simulations offer new avenues for creating dynamic and immersive learning experiences. Adaptive learning systems, powered by artificial intelligence, personalize the learning journey based on individual progress and performance.
Challenges and Future Trends:
While instructional design has come a long way, it faces challenges such as keeping pace with rapidly evolving technology, catering to diverse learner needs, and ensuring accessibility for all. The future of instructional design holds exciting possibilities, including the integration of augmented reality, gamification, and further advancements in adaptive learning.
In conclusion, instructional design stands as a dynamic and essential field, shaping the way we acquire knowledge and skills. As education continues to evolve, so too will the methodologies and technologies employed by instructional designers. Through a thoughtful and systematic approach, instructional design empowers learners to engage with content in meaningful ways, fostering a lifelong journey of discovery and growth. Books: SHOPNOW




Comments
Post a Comment